Approach A: Bitnami Installations Using System Packages
👆Identify whether the Bitnami stack uses native Linux system packages (Approach A),
or self-contained installation (Approach B) by running the command below:
bitnami@debian:~$ test ! -f "/opt/bitnami/common/bin/openssl" && echo "Approach A: Using system packages." || echo "Approach B: Self-contained installation."
To serve the application through the Apache web server with the mod_wsgi module,
follow the steps below.
Enable WSGI configuration for the Django application
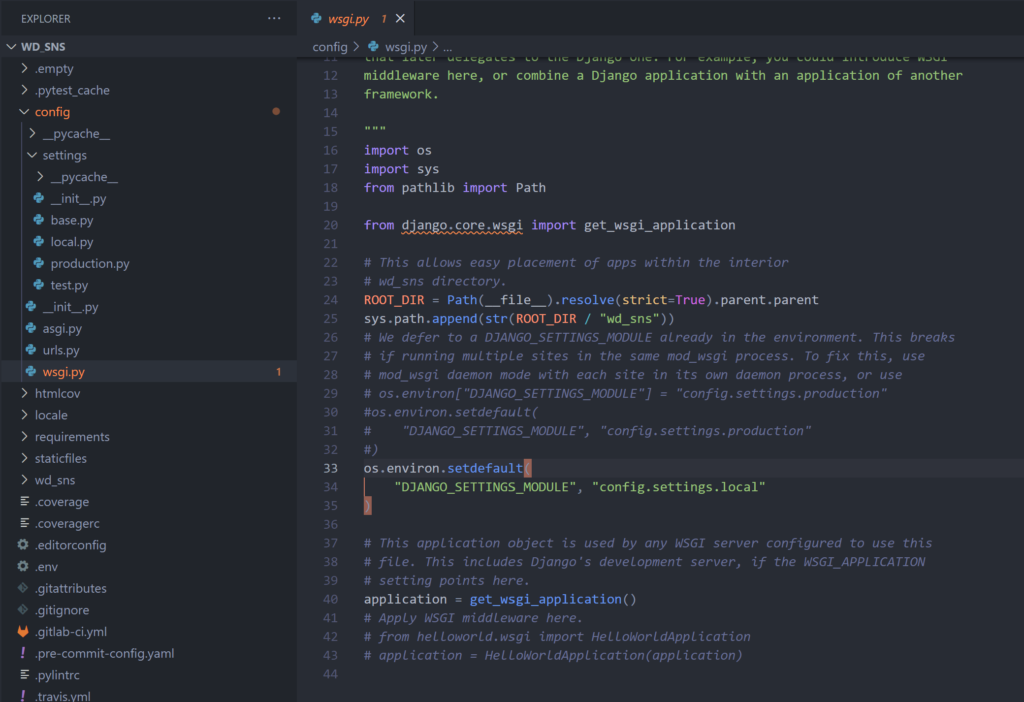
Ensure the Django project contains a wsgi.py file with contents similar to this:
import os
from django.core.wsgi import get_wsgi_application
os.environ.setdefault('DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE', 'PROJECT.settings')
application = get_wsgi_application()
Enable predefined virtual hosts for a Django project
The Bitnami installation comes with predefined HTTP and HTTPS virtual hosts for running Django projects
with the mod_wsgi module. To enable them, follow the steps below:
- Copy the files to remove the .disabled suffix:
NOTE: These files assume that the Django project is named sample
and is located at /opt/bitnami/projects/sample.
If your Django project is named or located differently, edit the
files below and update the file paths accordingly.
bitnami@debian:~$ sudo cp /opt/bitnami/apache2/conf/vhosts/sample-vhost.conf.disabled /opt/bitnami/apache2/conf/vhosts/sample-vhost.conf
bitnami@debian:~$ sudo cp /opt/bitnami/apache2/conf/vhosts/sample-https-vhost.conf.disabled /opt/bitnami/apache2/conf/vhosts/sample-https-vhost.conf

- Restart Apache for the changes to be taken into effect:
bitnami@debian:~$ sudo /opt/bitnami/ctlscript.sh restart apache
Ref:
Connect To The Virtual Machine From Another Host